AK Dutta1, S Bhardwaj2, HJ Sharma3.
1Director-Professor of Pediatrics, Kalawati Saran Children's Hospital, New Delhi,
2Medical Director, Serum Institute Of India Ltd., Pune,
3Deputy Medical Director, Serum Institute Of India Ltd., Pune. | | An Open, Randomized Phase III clinical trial to assess the efficacy of DTPw HB (Combination vaccine) and DTPw and Hepatitis B (Genevac B) vaccine alone, by separate site administration manufactured by Serum Institute of India Limited, Pune (INDIA) in comparison with standard commercially available DTPw HB vaccine. | | | | Abstract | Objective: To assess the immunogenicity and reactogenicity following administration of the DTPw HB vaccine (Combination vaccine of Serum Institute of India Ltd, Pune) alone and at separate site administration and its comparison with DTPw HB vaccine manufactured by Glaxo-Smithkline including local and systemic adverse events, in Indian children aged 6 - 14 weeks.
Design : Open, Comparative, Controlled Phase III Clinical trial
Study Site : Department of Pediatrics, Kalawati Saran Children's Hospital, New Delhi
Participants : 225 children (75 in each group) aged 6 - 14 weeks who received DTPw HB vaccine (Group A - SIIL), DTPw & HB (Group B - SIIL) vaccines at separate sites and DTPw HB vaccine (Group C - GSK) in a dose of 0.5 ml vial intramuscularly into the antero-lateral aspect of the left thigh using 25G 5/8" needle.
Intervention : Pre-vaccination screening of the subjects was done for HBs Ag positivity using ELISA technique. Pre-vaccination HBs Ag positive subjects were excluded from the study. Pre and post-vaccination (one month after the 3rd dose) IgG antibodies to D, T, P and anti-HBs components of the vaccine were determined by ELISA using standard commercially available kits with the cut off values, as mentioned in the kit literature.
Reactogenicity assessment : The following were assessed for reactogenicity : Pain, Redness, Swelling, Fever, Seizures, Hypotonic Hypo responsive episodes, Encephalopathy, Irritability, Unusual Crying, Drowsiness, Restlessness, Loss of appetite, Vomiting, Diarrhoea.
Results : In Group A (DTPw HB, SIIL), all 75 (100%) children became Sero-positive for IgG antibodies to Diphtheria, Tetanus and Anti HBs component whereas 73 children (97.33%) for Pertussis component. In group B (DTP & HB, SIIL), 71 children (98.66%) became positive for Diphtheria and 70 for Pertussis IgG anti bodies whereas all 72 (100%) became positive for IgG antibodies to Anti Tetanus and Anti HBs, Post-immunization. In group C (DTPw HB, GSK), 70 children (93.3%) became positive to IgG antibodies to Diphtheria component, 69 (92%) to Pertussis component, 74 (98.6%) to Tetanus and 73 (97.3%) children to Anti-HBs antibodies, post-immunization.
Conclusion : DTPw HB vaccine manufactured by Serum Institute Of India Ltd (Pune) is safe, efficacious and comparable to already registered commercially available DTPw HB Vaccine (GSK). | | | | Key Message | | Hepatitis B component does not interfere with the immune response to DTPw (whole cell) components of a quadrivalent vaccine. The combination vaccine retains the immunogenicity and safety profiles of the separate components and delivers good antibody concentrations with a variety of schedules. | | | | Introduction | Hepatitis B is one of the World's major health problems. (1) There are more than 300 million carriers of the virus worldwide. (2) Chronic sequelae of HBV infection include chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis of liver and hepato-cellular carcinoma. Vaccination of adults and children at high risk with Hepatitis B Vaccine has not controlled or reduced the prevalence of Hepatitis B. (3) The WHO assembly endorsed the recommendation made by its Global Advisory group that all countries should have an Hepatitis B immunization programme in place by the end of 1997, through the integration of HB Vaccination into the Expanded Programme for Immunization (EPI). (4) At least 47 countries have rational policies of routine Immunization of infants against Hepatitis B. (5) WHO /EPI's goal could be attained by combining Hepatitis B vaccine with DTPw vaccine, as there are no incompatibilities that would prevent the development of a tetravalent formulation. This strategy will make the control of Hepatitis B possible on a Worldwide basis. (5) International studies have also shown that the Hepatitis B component does not interfere with the immune response to DTPw (whole cell) components of a quadrivalent vaccine. (6) It is estimated that current vaccination coverage of infants with DTPw vaccine is about 72% globally. (7) Universal immunization of infants against these serious diseases remains a goal of the EPI. Various studies in the past have been conducted comparing the efficacy of this vaccine with the separately administered components by comparison of various administration schedules. (8-11) The combination vaccine retains the immunogenicity and safety profiles of the separate components and delivers good antibody concentrations with a variety of schedules. (12) Combination with a whole cell Pertussis vaccines enhances the serological response to Diphtheria and Tetanus toxoids because of the adjuvant properties of whole cell vaccines. (13)
With the above background the current study is planned to assess the immunogenicity and reactogenicity of DTPw HB (Combination Vaccine) indigenously manufactured by Serum Institute of India Ltd Pune administered alone or in combination & its comparison with standard commercially available DTPw HB vaccine in healthy Indian infants.
| | | | Methods & Materials | The objective of this study will be to assess the immunogenicity - efficacy following administration of the DTPw HB vaccine and also to assess the reactogenicity of the DTPw HB (Combination vaccine of Serum Institute of India Ltd, Pune) alone and at separate site administration and its comparison with standard commercially available DTPw HB vaccine of GSK including local and systemic adverse events, in Indian children aged 6 - 14 weeks. Pre- and post-vaccination (one month after the 3rd dose) IgG antibodies to D, T, P and anti-HBs components of the vaccine were to be determined by ELISA using standard commercially available kits with the cut off values, as mentioned in the kit literature. Pre-vaccination screening of the subjects was to be done for HBs Ag positivity using ELISA technique. Pre-vaccination HBs Ag positive subjects were excluded from the study
DTPw HB vaccine manufactured by Serum Institute of India was compared to assess its efficacy and safety in children aged 6, 10 and 14 weeks (+ 2 weeks) with the already registered commercially available vaccine of Glaxo Smithkline. Another comparison was made with DTPw and Hepatitis-B vaccine both manufactured by Serum Institute Of India, and given alone at separate sites and tested for their immunogenicity and reactogenicity. This comparison between DTPw HB (SIIL) and DTPw / HB (SIIL) given alone further signified the efficacy of the combination vaccine above individual vaccines administered at separate sites. Administration of these vaccines at 6, 10, 14 weeks (+ 2 weeks) of age is in accordance with the National immunization schedule in which the triple antigen is administered to all children.
The vaccinees were observed closely for at least 30 mins post-vaccination with appropriate medical treatment readily available in case of a rare anaphylactic reaction following vaccine administration.
During all these visits, subject's guardian were asked for the occurrence of any adverse events. In particular occurrences like Fever, Irritability, Unusual crying, Drowsiness, Restlessness, and any signs and symptoms suggestive of Loss of appetite, Vomiting, Diarrhoea, redness/ rash, swelling and Induration at the injection site were captured on the Case Report Form.
Any other adverse drug reactions (ADR) which occurred at any other time during the trial period, were notified to the investigator at a follow-up visit, and recorded by him in the CRF. If serious adverse events (SAE) developed, the parent / guardian of the subject were to consult the doctor immediately.
Ethical Considerations : The permission to conduct this study was granted by Drugs Controller General (India), New and the study was cleared by the Institutional Ethics Committee. Written, Explained Informed Consent in English / local vernacular language was obtained from the parents of the children after explaining nature of the study and its associated risks / benefits to them. Permission to draw the blood samples of their children to assess IgG antibody titres to D, P, T and Anti HBs, Pre & Post Immunization was also obtained. Pre-vaccination screening of the mothers was done for antibodies to HBsAg / HIV and all those with pre-vaccination HBsAg / HIV positivity were excluded from the study.
Microbiology: Whole blood samples (capillary or venous) were obtained from each subject at baseline and one month after the third vaccination dose in each group. 3 ml blood was obtained with scalp-vein sets and stored in vials. Haemolysed sera was discarded. Clear sera samples will be stored at -20°C prior to analysis and ELISA tests. Centralized Microbiological estimation was be performed at a certified laboratory, National Institute of Virology, Pune, India utilising standard commercially available kits with the cut off values as mentioned in the kit literature. | | | | Results | Subjects enrolled
Table I:- Group-wise distribution of subjects enrolled in the study
Vaccine |
DTPw HB (SIIL) |
DTPw & HB (SIIL) |
DTPw HB (GSK) |
Total |
Subjects enrolled |
115 |
110 |
100 |
325 |
Protocol completed |
75 |
75 |
75 |
225 |
Pre-vaccination sample |
115 |
110 |
100 |
225 |
Post-vaccination sample |
90 |
82 |
84 |
256 |
Sample lost |
- |
3 |
- |
3 |
Evaluable sample size |
75 |
72 |
75 |
222 |
Sex distribution
Table II : Sex-wise distribution in either of the study groups
Sex distribution |
Sex |
A (DTPw HB (SIIL)) |
B (DTPw & HB (SIIL)) |
C (DTPw HB (GSK)) |
Total |
Male |
43 (57.33%) |
48 (66.67%) |
52 (69.33%) |
143 (64.41%) |
Female |
32 (42.67%) |
24 (33.33%) |
23 (30.67%) |
79 (35.59%) |
Total |
75 (33.78%) |
72 (32.43%) |
75 (33.78%) |
222 (100%) |
Mean Age (in weeks)
In Group A {DTPw HB, SIIL( n=75)}, the mean age of children was 7.26 (±1.02) weeks. In Group B {DTPw & HB vaccine (n=72)}, the mean age of children was 7.30 (± 1.23) weeks whereas in Group C {DTPw HB (GSK), (n=75)} it was 7.25 (± 1.26) weeks.
Table III :- Group-wise distribution of the mean age (in weeks) of children (n=225)
Group |
n |
Mean (in weeks) |
Median |
S.D. |
A (DTPw HB (SIIL)) |
75 |
7.265 |
7 |
1.024 |
B (DTPw & HB (SIIL)) |
72 |
7.304 |
7 |
1.232 |
C (DTPw HB (GSK)) |
75 |
7.255 |
7 |
1.262 |
Mean weight (in kg)
Table IV :- Group wise distribution of Mean weight (in kgs)of subjects (n=225)
Group |
Birth weight (in kgs) |
Present weight (in kgs) |
|
Mean |
Median |
S.D. |
Mean |
Median |
S.D. |
A |
2.746 |
2.75 |
0.444 |
4.326 |
4.25 |
0.644 |
B |
2.74 |
2.75 |
0.444 |
4.447 |
4.5 |
0.68 |
C |
2.581 |
2.6 |
0.36 |
4.247 |
4.25 |
0.705 |
Nutritional Status
Table VI :- Group-wise distribution of subjects w.r.t. nutritional status (n=225)
Status |
Group |
A |
B |
C |
Poor |
8 (11%) |
5 (7%) |
10 (13%) |
Fair |
30 (40%) |
32 (44%) |
32 (43%) |
Good |
37 (49%) |
34 (47%) |
33 (44%) |
Excellent |
- |
1 (1%) |
- |
Note : Kruskal-Wallis test indicates that there is no statistical significant difference in the Nutritional Status between the three groups of vaccines (p=0.2846)
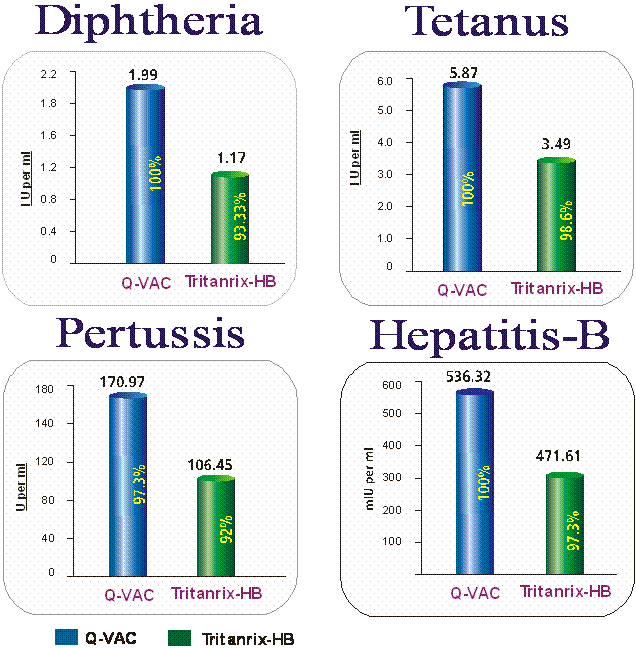
Geometric Mean Titres (Table VII) : IgG antibodies to Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis and HBsAg were estimated at baseline (Prevaccination) and one month after the last dose of the vaccine (Postvaccination). The difference between the pre-vaccination and Post-vaccination IgG antibody titres was highly significant in all three groups.
IMP : The table VII indicates the DTPw HB vaccine (Group A, SIIL) elicited higher IgG Antibody Geometric Mean Titres (GMTs) to Diphtheria, Pertussis Tetanus and Anti-HBs components of the vaccine when compared to DTPw HB vaccine (Group C, GSK) indicating that DTPw HB vaccine (SIIL) is of comparable immunogenicity to an already registered Tritanrix- HB vaccine (GSK).
Table VII : Immunogenicity Assessment in Each Treatment Group
| Group |
IgG antibodies (GMT ± SD) |
| |
Anti-Diphtheria (IU/ml) |
Anti-Tetanus (IU/ml) |
Anti-Pertussis (U/ml) |
Anti-HBs (mIU/ml) |
| Pre |
Post |
Pre |
Post |
Pre |
Post |
Pre |
Post |
Grp. A
(DTPw HB (SIIL))
(n=75)
|
0.07 |
1.99 |
1.21 |
5.87 |
16.93 |
170.97 |
1.94 |
536.32 |
| SD
(+) |
3.25 |
3.19 |
3.09 |
3.80 |
1.94 |
3.14 |
2.52 |
1.60 |
| 95% CI |
1.27-1.61 |
0.55-0.82 |
0.87-1.13 |
2.33-2.54 |
| p-value |
<0.0001, HS |
<0.0001, HS |
<0.0001, HS |
<0.0001, HS |
| Grp. B
(n=72) |
0.067 |
2.045 |
1.51 |
7.21 |
15.52 |
149.55 |
1.51 |
482.90 |
| SD (+) |
3.155 |
2.761 |
3.08 |
3.34 |
2.14 |
3.01 |
3.08 |
2.41 |
| 95% CI |
1.31-1.65 |
0.55-0.79 |
0.84-1.12 |
2.34-2.66 |
| p-value 95% CI |
<0.0001, HS |
<0.0001, HS |
<0.0001, HS |
<0.0001, HS |
|
(n=75) |
0.065 |
1.173 |
1.18 |
3.49 |
17.68 |
106.45 |
1.71 |
471.61 |
| SD (+) |
3.081 |
4.683 |
3.39 |
3.20 |
2.13 |
3.84 |
2.63 |
3.03 |
| 95% CI |
1.04-1.46 |
0.34-0.59 |
0.61-0.94 |
2.28-2.59 |
| p-value 95% CI |
<0.0001, HS |
<0.0001, HS |
<0.0001, HS |
<0.0001, HS |
* : Highly Significant
Reactogenicity assessment
For reactogenecity assessment, follow up for 4 weeks was done. The subjects were visited on days 1, 2, 3 and then once in rest of 1st week and then once a week upto, 4 weeks after each dose in all the three treatment groups. The most common adverse events noted after either of the vaccine's administered were as follows :-
Reactogenicity obseved |
Group A
(DTPw HB, SIIL) |
Group B
(DTPw & HB, SIIL) |
Group C
(DTPw HB, GSK) |
Pain |
34 (45.33%) |
30 (41.66%) |
36 (48%) |
Fever |
45 (60%) |
28 (38.88%) |
54 (72%) |
Redness |
1 (1.33%) |
2 (2.77%) |
- |
No Serious Adverse Event (SAE) was observed in either of the study groups. All of these subjects recovered within 48 hours with symptomatic treatment.
| | | | Conclusion | | Based on the above findings, it was concluded that DTPw HB vaccine manufactured by Serum Institute Of India Ltd (Pune) is safe, efficacious and comparable to already registered commercially available DTPw HB Vaccine. The results are also comparable to DTPw vaccine and Hepatitis B vaccine given at separate site concomitantly. | | | | Compliance with Ethical Standards | | Funding None | | | | Conflict of Interest None | | |
- Kane MA, Clements J, HuD. Hepatitis B in Disease Control priorities in Developing countries (Eds Jamison DT, Mosley WH, Meashan AR, Bobadilla J) World Bank Book, Oxford University Press, New York p 321-330, 1993.
- Park K. Text book of Preventive and Social Medicine, 15th Edition, p 159, 1997.
- Centers for Disease Control. Hepatitis B Virus - a comprehensive strategy for eliminating transmission in the United States through Universal childhood vaccination, recommendation of the Immunization Practices Committee (ACIP) MMWR, 40 (RR13), p 1 - 20, 1991.
- WHO. 45th World Health Assembly. Expanded programme on Immunization and Vaccine quality. Progress report by the Director General A 45/8, 9 April 1992.
- Kane M. Global programme for control of Hepatitis B infection. Vaccine 13 (Suppl 1) 547-549, 1995. [CrossRef]
- Javier Diez-Delgado, Rafael Dal-Re, Manual Llorente, Antonis Gonzalez & Jaun Lopez. Hepatitis B component does not interfere with immune response to diphtheria, tetanus and whole cell Bordetella Pertussis components of a quadrivalent (DTPw HB) vaccine: a controlled trial in healthy infants. Vaccine 15, No.12/13, p1418-1422, 1997. [PubMed]
- Expanded programme on Immunisation. Weekly Epidemiological Record No.1/2, Jan 11, 1991.
- Kanra G, Ceyhan M, Ecevit Z, et al. Primary vaccination of infants with a combined Diphtheria - Tetanus- Acellular Pertussis- Hepatitis B vaccine. Pediatr Infect Dis J 14:998-1000, 1995. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usonis V, Bakasenas V, Willems P, Clemens R. Feasibility study of a combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis acellular -Hepatitis B vaccine and comparison of clinical reactions and immune responses with Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis acellular and Hepatitis B vaccines applied as mixed or injected into separate limbs. Vaccine 15:1680-1686, 1997. [CrossRef]
- Giammanco G, Moiraghi A, Zotti C et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a combined Dpththeria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis-Hepatitis B vaccine administered according to two different primary vaccination schedules. Vaccine 16:722-726, 1998. [CrossRef]
- Greenberg DP, Wong VK, Partridge S, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a combination DTPa-Hep B administered to infants at 2,4 and 6 months of age. Abstracts of the 35th Annual Meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America;Arlington, Virginia;1997.
- Vaccines 521-522, Stanlin A. Plotkin, W.A.Orenstein, 1998.
- Vaccines 460, Stanlin A. Plotkin, W.A.Orenstein, 1998.
|
| Cite this article as: | | Dutta A, Bhardwaj S, Sharma H. An Open Randomized Phase III clinical trial to assess the efficacy of DTPw HB (Combination vaccine) and DTPw and Hepatitis B (GeneVac-B) vaccine alone by separate site administration. Pediatr Oncall J. 2005;2. |
|